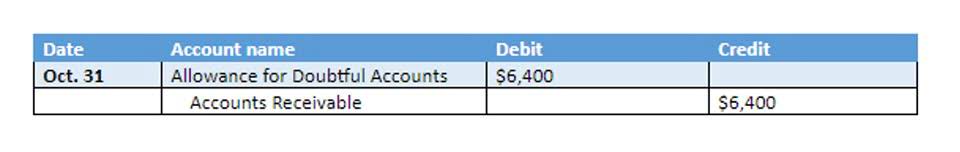
If the opposite is true — your tax liability is more than the amount withheld or paid through quarterly payments — you’ll have a tax bill. A customer uses the credit card to purchase an item that they do not have the cash for at that moment but will pay off in full later on. The debt incurred by the credit card is a liability because the business is obligated to repay all funds spent with interest. Recording a liability requires a debit to an asset or expense account (depending on the nature of the transaction), and a credit to the applicable liability account. When a liability is eventually settled, debit the liability account and credit the cash account from which the payment came. When evaluating the performance of a company, analysts like to see that any short-term liabilities can be completely covered by cash.
How to account for liabilities
This involves reconciling accounts, verifying outstanding obligations, and addressing any discrepancies promptly. Most contingent liabilities are uncommon for small businesses, but here are some that income summary you might encounter. US GAAP requires some businesses to disclose or report contingent liabilities.

Question 6: what are some examples of long-term liabilities?
- The interest portion of the repayments would be posted to the interest expense and interest payable accounts.
- Short term liabilities cover any debt that must be paid within the coming year.
- Our writing and editorial staff are a team of experts holding advanced financial designations and have written for most major financial media publications.
- These liabilities may or may not materialize, and their outcome is often uncertain.
- As the company makes payments on the mortgage, the principal portion of the payment reduces the mortgage payable, while the interest portion is accounted for as an interest expense.
Listed in the table below are examples of current liabilities on the balance sheet. Liabilities are a vital aspect of a company because they’re used to finance operations and pay for large expansions. They can also make transactions between businesses more efficient. A wine supplier typically doesn’t demand payment when it sells a case of wine to a restaurant and delivers the goods. It invoices the restaurant for the purchase to streamline the drop-off and make paying easier for https://www.bookstime.com/ the restaurant. Liabilities are categorized as current or non-current depending on their temporality.
How Are Current Liabilities Different From Long-Term Non-Current Ones?
- Liabilities are probable non-ownership claims against a business firm.
- The outstanding money that the restaurant owes to its wine supplier is considered a liability.
- You also must record a utility liability for the amount you owe until you actually pay it.
- Recording a liability requires a debit to an asset or expense account (depending on the nature of the transaction), and a credit to the applicable liability account.
- Answering the first question requires that the accountant determine the likelihood that the payment will be made.
- Many first-time entrepreneurs are wary of debt, but for a business, having manageable debt has benefits as long as you don’t exceed your limits.
- Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader.
An operating lease is recorded as a rental expense, while a finance lease is treated as a long-term liability and an asset on the balance sheet. Accounts Payable refers to the amounts owed by a company to its suppliers or vendors for goods or services received, but not yet paid for. Examples include invoices from suppliers, utility bills, and short-term debts. Accounts payable is typically presented on the balance sheet as a separate line item under current liabilities.

Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists

Examples – trade creditors, bills payable, outstanding expenses, bank overdraft etc. Examples of liabilities are accounts payable, accrued liabilities, accrued wages, deferred revenue, interest payable, and sales taxes payable. Any liability that’s not near-term falls under non-current liabilities that are expected to be paid in 12 months or more. Long-term debt is also known as bonds payable and it’s usually the largest liability and at the top of the list.
How do we recognize a liability on a balance sheet?
- A liability account is a category within the general ledger that shows the debt, obligations, and other liabilities a company has.
- For information pertaining to the registration status of 11 Financial, please contact the state securities regulators for those states in which 11 Financial maintains a registration filing.
- Contingent liabilities are potential future obligations that depend on the occurrence of a specific event or condition.
- Examples of liabilities are accounts payable, accrued liabilities, accrued wages, deferred revenue, interest payable, and sales taxes payable.
- More specifically, liabilities are subtracted from total assets to arrive at a company’s equity value.
- In very specific contract liabilities, failure to pay on the installment date will produce penalties, and such penalties can also be considered a cost of having liabilities.
Our popular accounting course is designed for those with no accounting background or those seeking a refresher. We strive to empower readers with the most factual and reliable climate finance information possible to help them make informed decisions. This team of experts helps Carbon Collective maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. Our team of reviewers are established professionals with years of experience in areas of personal finance and climate. Carbon Collective partners with financial and climate experts to ensure the accuracy of our content. Bob from Bob’s Donut Shoppe what is liability account Inc takes out a $100,000 loan from a bank over 10 years.
